Asia-Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching, Volume 16, Issue 2, Article 8 (Dec., 2015) |
Findings Related to Between PSI, SPST and TOLT Pre-test Scores
Independent t-tests were used to analyze the data obtained from pre-test treatments. The results are given in Table 1.
Table 1. The pre-test scores of prospective science teachers in both groups
Pre-test Scores Groups
N
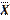
SD
Df
t
p
PSI
Experimental
50
78.44
11.43
96
-.539
.591
Control
48
79.60
9.86
SPST
Experimental
50
72.05
11.85
96
.221
.826
Control
48
71.52
11.76
TOLT
Experimental
50
5.42
1.61
96
-.104
.918
Control
48
5.45
2.03
When Table 1 is examined, it can be seen that there is no significant difference between the perception levels of problem solving ability, between the science process skills and between the skills of logical thinking pre-test scores of prospective science teachers in both the experimental group and the control group (p>α).
According to the scores in Table 1 it was observed that the experimental group and control group are equivalent with respect to their science process skills, skills of logical thinking and the perception levels of problem solving skills at the beginning of the study.
Findings to MANCOVA Analysis
MANCOVA analysis was performed in order to examine the effect of two different methods on the perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills of prospective teachers. The perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills of prospective teachers before the applications were considered as “common variables”; the perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills of prospective teachers after applications were considered as “dependent variables”; and both methods which were used were considered as “independent variables.” Within the realized analysis, first it was examined whether the regression lines calculated. The obtained results, that p=.931>α=.05, indicated that the calculated regression lines were equal. After the hypothesis of equality of regression lines was tested, descriptive statistics regarding both realized method types and the perception level of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills obtained after applications were determined and related results were shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Descriptive statistics of the past-test scores of PSI, SPST and TOLT
Past-test Scores Group
N
Mean
Std. Deviation
SPST
Experimental
50
78.7786
7.95194
Control
48
71.4325
9.75433
Total
98
75.1805
9.57442
TOLT
Experimental
50
6.8400
1.83348
Control
48
5.6458
1.87355
Total
98
6.2551
1.93881
PSI
Experimental
50
69.4600
8.77196
Control
48
77.2500
7.61717
Total
98
73.2755
9.07220
That p=.724>α=.05, according to the results obtained after the examination of the hypothesis of the equality of covariance matrixes within the scope of the study, indicated that this hypothesis was verified. Again within the scope of the study, for the perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills and both performed methods, p<α involved in Wilks’ Lambda lines provided preliminary information that these variables (pre-applications variables and application type) had an effect on dependent variables. The condition of p>α in the results obtained after the Levene test, made to test the hypothesis of the equality of error variables, demonstrated that this hypothesis was verified.
The perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills of prospective science teachers were synchronized with MANCOVA before the applications and it has been demonstrated how the applied method types affected the prospective teachers after applications in Table 3.
Table 3. Tests of between-subjects effects
Source Dependent Variable
Type III Sum of Squares
df
Mean Square
F
Sig.
Partial Eta Squared
Corrected Model
SPST_PastTest
5651.526(a)
4
1412.881
40.550
.000
.636
TOLT_PastTest
228.537(b)
4
57.134
39.045
.000
.627
PSI_PastTest
6978.713(c)
4
1744.678
161.472
.000
.874
Intercept
SPST_PastTest
860.935
1
860.935
24.709
.000
.210
TOLT_PastTest
.203
1
.203
.139
.711
.001
PSI_PastTest
13.482
1
13.482
1.248
.267
.013
SPST_PreTest
SPST_PastTest
3428.005
1
3428.005
98.384
.000
.514
TOLT_PastTest
6.161
1
6.161
4.210
.043
.043
PSI_PastTest
4.070
1
4.070
.377
.541
.004
TOLT_PreTest
SPST_PastTest
113.631
1
113.631
3.261
.074
.034
TOLT_PastTest
148.331
1
148.331
101.368
.000
.522
PSI_PastTest
9.387
1
9.387
.869
.354
.009
PSI_PreTest
SPST_PastTest
18.668
1
18.668
.536
.466
.006
TOLT_PastTest
.001
1
.001
.000
.983
.000
PSI_PastTest
5399.705
1
5399.705
499.750
.000
.843
Group
SPST_PastTest
990.553
1
990.553
28.429
.000
.234
TOLT_PastTest
29.827
1
29.827
20.384
.000
.180
PSI_PastTest
1122.880
1
1122.880
103.924
.000
.528
Error
SPST_PastTest
3240.411
93
34.843
TOLT_PastTest
136.086
93
1.463
PSI_PastTest
1004.848
93
10.805
Total
SPST_PastTest
562798.630
98
TOLT_PastTest
4199.000
98
PSI_PastTest
534175.000
98
Corrected Total
SPST_PastTest
8891.936
97
TOLT_PastTest
364.622
97
PSI_PastTest
7983.561
97
a R Squared = .636 (Adjusted R Squared = .620)
b R Squared = .627 (Adjusted R Squared = .611)
c R Squared = .874 (Adjusted R Squared = .869)It was demonstrated that both application types affected the perception levels of problem solving ability, scientific process skills and logical thinking skills of prospective teachers after the applications (p<α). Also, when eta square values were examined, it was seen that 52% of the change in the perception level of problem solving ability, 23% of the change in the level of scientific process skill and 18% of the change in the level of logical thinking skill in prospective teachers resulted from the applied application type.
Finally, the averages of the perception levels of problem solving ability, the levels of scientific process skill and the levels of logical thinking skill of prospective teachers after the applications were demonstrated, as seen in Table 4.
Table 4. Estimated marginal means
Dependent Variable
Group
Mean
Std.Error
95% Confidence Interval
Lower Bound
Upper Bound
SPST_PastScores
Experimental
78.310(a)
.837
76.648
79.971
Control
71.921(a)
.854
70.225
73.617
TOLT_PastScores
Experimental
6.798(a)
.171
6.458
7.139
Control
5.689(a)
.175
5.342
6.037
PSI_PastScores
Experimental
69.944(a)
.466
69.019
70.869
Control
76.746(a)
.476
75.802
77.690
a Covariates appearing in the model are evaluated at the following values: SPST_PreScore = 70.6635, TOLT_PreScore = 5.3878, PSI_PreScore = 78.3367.
The post-test results of the both applications displayed in Table 4 indicated that while the pre-test score of a prospective teacher regarding their perception level of problem solving ability was 78.33, it decreased down to 69.94 after the PSASL. The low scores obtained from PSI indicate effective problem solving abilities, while the high scores indicate failure to find effective solutions to problems (Taylan, 1990). Likewise, what the scientific process skill and logical thinking skill of a prospective teacher with a level of 70.66 and 5.38 before the applications may become after being subjected to both applications was given in Table 4. In this case it can be said that the PSASL application is more effective than the traditional laboratory application type, which is a more research-oriented application on the perception levels of problem solving ability, the levels of scientific process skill and of logical thinking skill of prospective teachers.