Asia-Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching, Volume 21, Issue 1, Article 8 (Dec., 2021) |
This study obtained 63 calculated effect sizes from 22 studies using 7,258 samples. Descriptive features of the studies are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of effect size value
Researcher
Num
(k)Year
Types of Science Subject
Category of SRL
SRL Strategy
Effect size
(d)DiBenedetto & Bembenutty
113
2013
Science
B
ADOG
HSR
HS0.52
0.39
0.39Olakanmi & Gumbo
60
2017
Chemistry
ME&C
GS
4.95
Medina & Pagan
30
2016
Science
ME&C
SM
0.31
Al Mutawah et al.
382
2017
Science
MO
GO
TV
SE0.41
0.38
0.52Peter & Kitsantas
162
2010
Science
ME&C
O
E0.50
0.80Sebesta & Bray Speth
414
2017
Biology
ME
MO
OT
GSP
SI
SE
KEM
ES
SC
RA
SA
SIA
SA
RN
RE
RT
RGW0.18
0.25
0.24
0.30
0.11
0.09
0.23
0.09
0.15
0.16
0.24
0.25
0.32
0.17
0.22Kaberman & Dori
793
2009
Chemistry
ME
PQ
0.70
Dike et al.
360
2017
Chemistry
ME
TA
0.97
Nbina & Viko
192
2010
Chemistry
ME
SA
4.36
Akyol& Tekayya
1517
2010
Science
ME
R
E
O
C0.01
0.05
0.05
0.01Jayapraba
35
2013
Science
C
MSR
0.06
Ibe
21
2009
Science
ME
MQ
0.74
Theresa et al.
50
2019
Chemistry
ME
RT
4.75
Cook et al.
595
2013
Chemistry
ME
L
0.65
Nongtodu & Bhutia
797
2017
Science
ME
L
0.94
Yumusak et al.
519
2007
Biology
MO
ME
C
IGO
EGO
TV
CVLR
SE
ER
PL
HL
MSRT
MRSE
R
E
O
CT0.46
-0.28
0.83
0.12
0.6
0.84
0.39
0.29
0.60
0.69
0.49
0.17
0.65
0.41Veluu et al.
358
2015
Chemistry
C
CT
0.05
Lawanto & Santoso
97
2013
Physics
ME
NT
0.43
Laureano
70
2015
Chemistry
B
R
Ev
T
S
F
I
A0.36
0.26
0.06
0.04
0.06
0.004
0.04Sadi
384
2017
Biology
C
R
0.08
Joo et al.
152
2000
Science
MO&C
SE
0.41
Harowitz et al.
157
2013
Chemistry
B
HS
0.69
ME Metacognitive, C Cognitive, MA Management, MO Motivation, B Behaviour, HP Help Seeking, SM Self-monitoring, SR Self-reflection, SE Self-evaluation, M Management, OI Organisation Information, GO Goal Orientation, TV Task Value, SE Self-efficacy, TA Thinking Aloud, R Rehearsal, E Elaboration, RE Researching, T Triggering, CT Critical Thinking, Ev Evaluation, MSR Metacognitive Self-regulation, ME Metacognitive Question, RT Reflective Thinking, F Formulating, I Implementing, IGO Intrinsic Goal Orientation, EGO Extrinsic Goal Orientation, MSRTSE Metacognitive Self-regulation and Study Environment, A Assessing, ER Effort Regulation, PL Peer Learning, II Interpretation Information, RI Representation Information, ADOG Academic Delay of Gratification, HSR Homework Self-regulation.
Effects of Self-Regulated Learning Strategies
The results showed a significant effect, with an overall mean effect of d =12. This finding suggests that SRL learning strategies improve students’ achievement in science subjects.
Effects of Moderator Influence
There were significant effects of moderator influence on students’ achievement (see Table 1). The effect size was varied depending on the study setting, educational level, and types of science subject. Figures 1 and 2 show the details of the results.
Categories of Self-regulated Learning Strategies
The overall mean effect for the eight categories of SRL was d=0.4, which was considered a medium effect. The total effect size for the first category which is metacognitive was d=15.6; for the second category which is cognitive, it was d=0.4; and for the third category which is behavioural, it was d=6.7. Meanwhile, for motivational strategy, which is the fourth category, the total effect size was d=1.3. For the combination of metacognitive and cognitive, the total effect size was d= 6.6; for the combination of metacognitive, cognitive, and motivational, it was 15 (d=7.0), while for the combination of metacognitive and motivational, it was d=3.0, and for the last category which is a combination of motivational and cognitive, the total effect size was d=3.0. Figure 1 shows the mean effect for each category in detail.
Based on the analysis, the self-regulated learning strategies were categorised into eight main SRL categories. Category 1 (metacognitive strategy) comprised i) posing question, ii) thinking aloud, iii) self-assessment, iv) metacognitive questions, v) Know, Want to know and Learn (KWL), vi) lecture, and vii) note taking. Category 2 (cognitive strategy) included i) rehearsal, ii) elaboration, iii) organisation, and iv) critical thinking. Meanwhile, Category 3 (behaviour strategy) consisted of i) academic delay of gratification, ii) homework self-regulation, iii) help seeking, iv) triggering, v) formulating, vi) searching, vii) implementing, vii) receiving, ix) evaluating, and x) assessing. Category 4 (combination of cognitive and metacognitive) included i) goal setting, self-monitoring, and self-reflection, ii) combination of self-monitoring strategies, self-evaluation strategies, self-reflection strategies and teachers’ feedback, iii) combination of rehearsal, elaboration, organisation, critical thinking, and metacognitive self-regulation strategy, v) combination of organisation information, teachers’ feedback, interpretation of information, and vi) combination of content self-evaluation, self-monitoring, and think aloud. Category 5 (combination of metacognitive and motivational) comprised combination of self-evaluation, organising and transferring, goal setting and planning, seeking information, keeping records and monitoring, environmental structuring, self-consequating, rehearsal and memorising, seeking assistance from other resources, reviewing notes, reviewing exams, reviewing textbooks/screencast, and reviewing graded work. Category 6 (combination of cognitive, metacognitive, and motivational) included i) combination of intrinsic goal orientation, extrinsic goal orientation, task value, control of learning beliefs, self-efficacy for learning and performance, and test anxiety. Lastly, Category 7 (combination of motivational and cognitive) comprised i) combination of cognitive strategy, self-efficacy, and self-regulation.
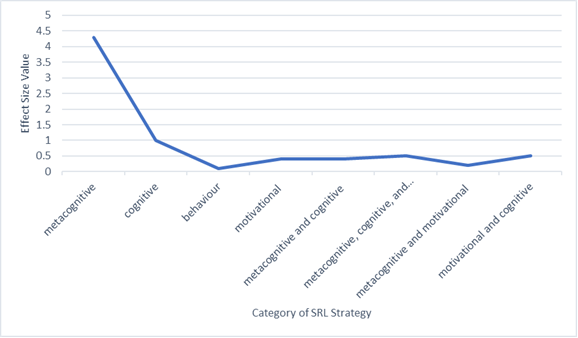
Figure 2. Categories of SRL strategy
Based on Figure 2, the overall mean effect for the categories of self-regulated learning strategies according to subject was 0.7, which was considered a large effect. Specifically, the mean effect for metacognitive was d=1 (large effect); for cognitive, it was d=0.1 (small effect); and for behaviour, the mean effect was d=0.3 (small effect). Meanwhile, for motivational, the mean effect was d=0.4 (medium effect); for metacognitive and cognitive, it was d=0.4 (medium effect); and for metacognitive, cognitive, and motivational, it was d=0.5 (medium effect). The mean effect for metacognitive and motivational was d=0.2 (small effect), and for the last category, which is motivational and cognitive, the mean effect was d=0.5 (medium effect).
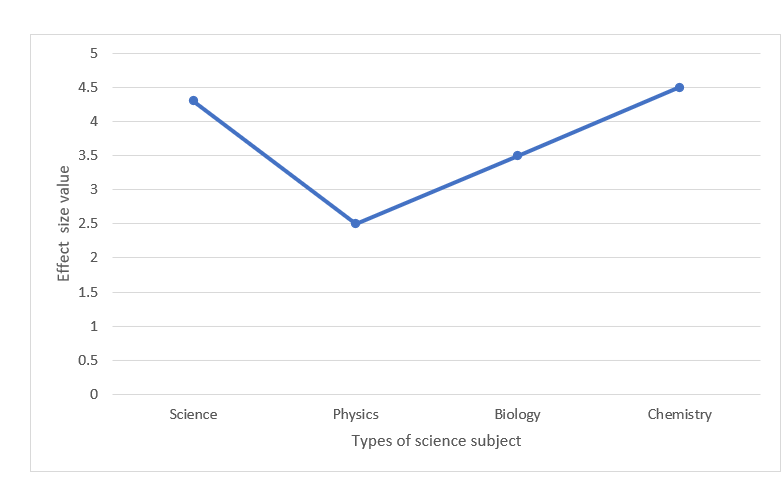
As shown in Figure 3, the mean effect size was found to be different based on the types of science subjects. The overall mean was d=0.6, which was considered a large effect. The total effect size for science was (d=17.8,28), while for chemistry, it was (d=19.2,14). Meanwhile, for biology and physics the total effect size was (d= 9.6,11) and (d=0.4.8,1), respectively.
Figure 3. The mean of effect size