Asia-Pacific Forum
on Science Learning and Teaching, Volume 11, Issue 2, Article 5 (Dec., 2010) |
Method
In this study, the quasi-experimental research design consisting of an experimental group (EG) and a control group (CG) is used (Cohen & Manion, 1994; Çepni, 2007). Each group is given both a pretest and a posttest. In the study, a delayed posttest was also implemented to both CG and EG students in addition to the pretest and posttest. The same science teacher taught both groups. The EG is taught with teaching materials based on the 5E instructional model, prepared for the elementary school's 8th grade floating and sinking subject in the “Force and Motion” unit. These teaching materials are enriched with different teaching methods and techniques (POE, Worksheets, CCT, CC and Animations). The CG is taught with the existing textbook materials developed by the Ministry of Education based on the 5E instructional model of the constructivist theory. After the pilot study (240 min), implementation of the main research took 6 course hours (240 min).
The sample
48 students, 25 EG and 23 CG from the 8th grade students (14–15 years), formed the sample. Six groups, which were socially and economically similar to each other, were formed within the EG and CG. Students were selected according to their achievement scores from The Level Determination Exam (LDE). Experimental group (EG) students are coded as E1, E2, E3,….., E25. Control Group (CG) students are coded as C1, C2, C3,……, C23.
Data collection tool
Students’ alternative conceptions, for both the EG and CG, were determined by using three two-tiered questions from the two-tiered Determining Differentiation in Conceptual Structure Test (DDCST) prepared by Şahin (2010). Its Cronbach’s Alpha reliability coefficient is 0.81. These questions were applied to the sample as pretest, posttest and delayed posttest. The first-tier of each item consists of a content question having four choices; the second part of each item contains reasons for the answer given in the first-tier response. As a data-collecting tool, 3 two-tier questions were used in this study. The first question is asked to determine whether the study sample has the common alternative conceptions about floating and sinking from the literature. The second question is asked to examine students’ ideas about the position of objects in the liquid related to the case of floating and sinking. The third question is asked to compare the density of subject with the density of the fluid for determining their conceptual structure related to buoyancy force with fluid density.
Data analyses
Researchers used different categories for evaluating students' levels of understanding (Abraham, Gryzybowski, Renner & Marek, 1992; Haidar & Abraham, 1991; Marek, 1986). Abraham et al. (1992), gave the final form to the understanding level categories often used in various studies such as “no understanding,” “specific misconception,” “partial understanding together with a specific misconception,” “partial understanding” and “full understanding” categories and gave were given points 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. These categories are based on and used in the subsequent studies (Çalık, Ayas & Coll, 2010; Özsevgeç, 2007).
In this study scoring categories created by Şahin (2010) are used to analyse the levels of differentiaon in conceptual structures. According to the scoring categories created by Şahin (2010), first stage of the two-tiered questions were analysed under three categories as a correct choice (CC), incorrect choice (IC) and empty (E). CC pointed as 5, IC pointed as 1 and E is pointed as 0. In order to distinguish the IC category from the E category, a 0 point is not given to the IC category. If students receive the IC category it doesn't mean that they do not know anything. In order to identify a significant difference between students choosing the CC and IC, 5 points are given to the CC category. At the beginning, 10 of the students’ qualitative responds were examined and the emerged situations were regarded while analysing the qualitative responses of second phase of the two-tiered test of students. Then, categories like correct reason (CR), partial correct reason (PCR), reason including alternative concepts (RIAC), incorrect reason (IR) and unrelated reason/empty (UR) were established for students understanding level and were aligned and marked according to their importance. Categories used to analyse the second phase of two-tiered questions; their points and content were presented in Table II.
Table II. The used categories for analyzing of two-tier questions, the points and index of the categories
Understanding Level/ Abbreviation
Points
Index
Correct Reason / (CR)
10
Answers including all aspects of the validity reason
Partially Correct Reason / (PCR)
8
Answers don’t include all aspects of the validity reason, just includes some aspect.
Reason Including Alternative Concept / (RIAC)
3
Answers including partially correct knowledge and misconceptions in the explanation.
Incorrect Reason / (IR)
2
Answers including incorrect knowledge.
Unrelated Reason / Empty (UR)
0
Answers including unrelated reason,
Answers not showing the relationship with the question
To avoid or write just the questions as answers.Eleven categories scores, which were used in data analysis, were gathered by adding the points of the first and second stages of two-tiered questions. Expressing the reason for marking the first stage true or partly true is more important than just marking the correct choice; so CC, PCR, RIAC categories are in front of the IC category. As all the questions in the questionnaire were categorised in CC-CR category, the highest total points that students can take is (15x3) 45.
Statistical analyses were done after the data collected from the two-tiered questions were classified and marked. The non-parametric Wilcoxon Signed rank test for related samples and the Mann-Whitney U test for independent samples were used for data analyses. As two-tiered questions are a kind of classified scale, and the data doesn't show normal dispersion, the non-parametric analysing technique was used in this study (Özdamar, 2004).
Table III. Categories, abbreviations and points used to classify students' answers
Categories
Abbreviation
Points
Correct Choice - Correct Reason
CC- CR
15
Correct Choice - Partially Correct Reason
CC-PCR
13
Incorrect Choice - Correct Reason
IC-CR
11
Incorrect Choice - Partially Correct Reason
IC- PCR
9
Correct Choice - Reason Including Alternative Concept
CC- RIAC
8
Correct Choice - Incorrect Reason
CC- IR
7
Correct Choice - Unrelated Reason / Empty
CC- UR
5
Incorrect Choice -Reason Including Alternative Concept
IC-RIAC
4
Incorrect Choice - Incorrect Reason
IC-IR
3
Incorrect Choice - Unrelated Reason / Empty
IC-UR
1
Empty - Unrelated Reason / Empty
E-UR
0
Pilot study
A pilot study is conducted covering 30 8th grade elementary school students (six groups) and their science teachers. Applicability of the developed teacher guided material and instructional material was examined during the pilot study. Researchers provided only technical support to the science teacher in the implementation process of the teaching materials.
Implementation of the study
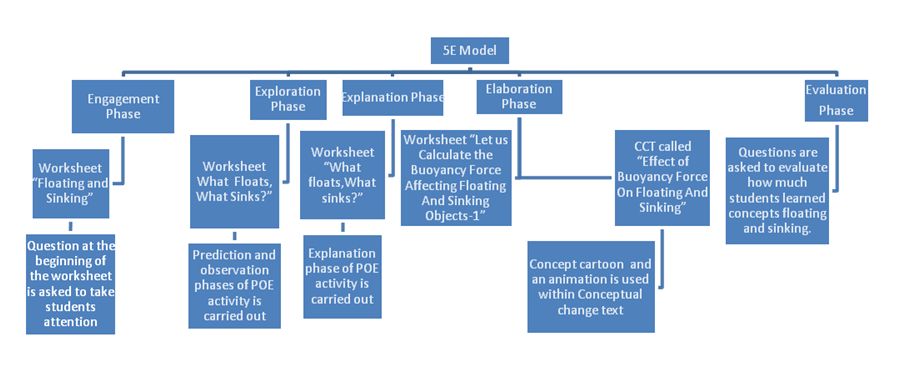
Implementation process of the prepared material is given below in Figure 1.
Figure 1.Theoretical framework of the developed teaching material
In this study, worksheets were prepared to implement activities in a certain order and were enriched with the teaching methods and techniques (CCT, CC, animations, worksheets and POE) for effective implementation of each phase of the 5E instructional model. Five worksheets were prepared. One worksheet is presented in Appendix 1. Teacher guided material containing a detailed explanation about the usage of the material applied in the study is given in Appendix 2. Animation screen views are given as an example in Appendix 3. The same science teacher did the applications to the both the EG and CG. The applications were completed in the same period and amount of time for both groups. The developing material according to the 5E instructional model enriched with different teaching methods and techniques was applied to the EG. The workbook and course book were prepared according to the 5E instructional model recognized by the Ministry of Education were applied to the CG.